Blood feels like one of those things everyone has in common. We talk about blood types casually, usually when donating or filling out medical forms. Most people know whether they are A, B, AB, or O, and maybe whether they are positive or negative. Yet behind those familiar labels sits a medical reality so rare that only a few dozen people worldwide live with it. Known as Rh-null and often called golden blood, it is widely considered the rarest blood type on Earth.
At first, it almost sounds unreal. Like something mentioned in a textbook footnote or a trivia question. But the reality is that this blood type can save lives that no other blood type can. At the same time, it places its carriers at constant medical risk.
What Blood Types Really Mean
Blood types are not labels added for convenience. They are based on physical markers, called antigens, that sit on the surface of red blood cells.
The system most people know is ABO. That determines whether someone is type A, B, AB, or O. Alongside it is the Rh system, which is more complex. It includes dozens of antigens, not just one. The best known is the D antigen, which determines whether someone is Rh-positive or Rh-negative.
Most people carry several Rh antigens, even if they are labeled Rh-negative. Rh-null blood differs in a particular way. It completely lacks all Rh antigens. Not a few of them. Every single one. That total absence is what makes this blood type so unusual and so difficult to manage.
Why Rh-Null Is Called Golden Blood
The nickname golden blood did not originate from color or status. It came from value. Rh-null blood can be safely given to people with rare Rh-related conditions who would otherwise reject almost all other blood types.
In transfusion medicine, compatibility matters more than anything else. Some patients develop antibodies that attack Rh antigens. For them, even Rh-negative blood can cause dangerous immune reactions. Rh-null blood avoids this problem because there are no Rh antigens to trigger an attack.
Because of that, one unit of Rh-null blood can save a life when no other option exists. Doctors sometimes describe it as priceless.
But there is a hard reality attached. People with Rh-null can only receive Rh-null blood themselves. There is no substitute waiting in reserve.
Just How Rare Is the Rarest Blood Type?
Rarity is often overstated in headlines. In this case, it is not. Fewer than 50 people worldwide are known to have true Rh-null blood. The number shifts slightly over time, but it remains incredibly small.
This scarcity comes from genetics. Rh-null usually results from inherited mutations that stop the body from producing Rh antigens. In many known cases, it appears in families where parents share close genetic ties, which increases the chances of rare traits being passed down.
Because it is inherited, Rh-null often stays hidden. Many people only learn about it after a medical emergency, a transfusion reaction, or complications during pregnancy. In that way, golden blood often reveals itself by accident.
How Missing Antigens Affect the Body
It is easy to think that missing antigens only matter during transfusions. That is not entirely true. Rh antigens also help keep red blood cells stable as they move through the bloodstream.
Without them, red blood cells can be more fragile. They may break apart more easily while circulating. Over time, this can lead to mild or moderate anemia.
Some people with Rh-null experience fatigue or weakness. Others may notice jaundice from increased red cell breakdown. Symptoms vary widely, and carriers feel almost nothing, while others need ongoing monitoring. This fragility is one reason doctors follow people with golden blood closely, even when no transfusion is expected.
Transfusions Become a High-Risk Puzzle
For most patients, a blood transfusion is routine. For someone with Rh-null, it becomes a logistical challenge with global consequences.
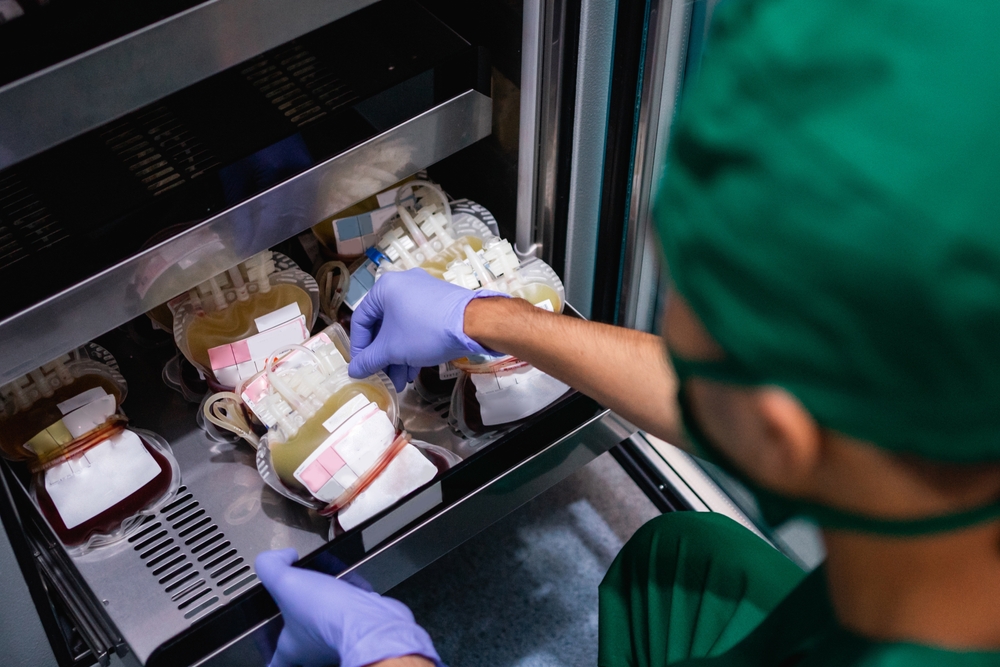
Hospitals do not keep Rh-null blood on hand. Instead, known donors are registered in international rare blood databases. Their blood is collected, frozen, and stored under strict conditions for many years.
If a person with Rh-null suddenly needs blood, doctors may need to coordinate across borders within hours. Blood must be located, transported, thawed, and matched exactly, leaving little room for error.
Because of this risk, people with the rarest blood type are often encouraged to donate regularly when healthy. In many cases, their own stored blood may be what saves them later.

The Emotional Weight of Medical Rarity
Living with an ultra-rare condition comes with emotional consequences that are easy to overlook. People with golden blood often describe feeling different in ways that never fully fade.
Some feel like a walking emergency. Others feel pressure knowing their blood might be needed to save someone else. Travel can be stressful. An accident far from a major hospital becomes a serious concern. Even planned surgeries require careful coordination and advance notice.
Pregnancy Complications and Genetic Risks
Pregnancy introduces another level of complexity. Rh incompatibility already affects many pregnancies. With Rh-null, those risks can be harder to manage.
If a fetus inherits Rh antigens from the other parent, the mother’s immune system may see the baby’s blood as foreign. This can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn if not monitored carefully.
Because of this, pregnancies involving Rh-null usually require specialized care and close follow-up. Genetic counseling is often recommended, especially in families where the condition has appeared before. With proper medical support, healthy pregnancies are possible, and careful planning remains essential.
How Rare Blood Shapes Emergency Planning
Emergency planning looks very different for people with golden blood. Most healthcare systems rely on backups. If one unit is unavailable, another usually is. With Rh-null, that safety net does not exist.
Doctors often work with patients long before emergencies happen. Plans may include medical alert bracelets, detailed hospital records, and written transfusion instructions. Some people even travel with documentation explaining their blood type.
These steps may seem extreme, but for those living with golden blood, they are practical. When time matters, preparation reduces risk.
The Role of Blood Donation in a Global Network
Blood donation carries a different weight when the supply is so limited. For Rh-null donors, each donation has a potential global impact.
Doctors schedule donations carefully to protect donor health. Blood is frozen using special methods that allow long-term storage. This makes it possible to respond to emergencies many years later.
A donation given today might never be used. Another might save a life on the other side of the world. Donors live with that uncertainty, and many describe pride mixed with caution. Helping others matters, but personal health comes first.
Why Scientists Study Extremely Rare Blood Types
Rare blood types offer insights that science cannot easily recreate. Studying Rh-null shows what happens when specific proteins are completely absent from red blood cells.
Researchers learn how cell membranes stay stable. They also learn why immune systems react so strongly to unfamiliar antigens. This research does not stay limited to rare cases. It improves transfusion safety and helps explain immune-related blood disorders.
Public Awareness and Common Misunderstandings
Golden blood attracts attention because it sounds dramatic. That attention often leads to misunderstandings. Some people assume it means better health or special abilities. Others think it offers protection, but none of that is true.
Rh-null does not make life easier. In many ways, it complicates healthcare. Clear information helps reduce fear and unrealistic expectations. For families affected by Rh-null, awareness can also help explain medical needs to others.
The Strength of People Living With Golden Blood
People with rare conditions often learn resilience early, and those with Rh-null are no different. They learn to explain their blood type and double-check forms. They ask more questions than most patients. Over time, this becomes routine.
Despite the risks, most live full lives. They work, travel, raise families, and plan futures. Awareness shapes their choices, not fear.

Ethical Questions Around Rare Blood Use
The value of golden blood raises difficult questions. Who decides when it is used, and how it is prioritized if more than one patient needs it?
Blood banks rely on ethical frameworks. Medical urgency and likelihood of benefit often guide decisions. Even then, choices can feel tough. Healthcare workers and donors both carry that weight. In rare blood medicine, decisions are rarely simple.
Read More: How Your Blood Type May Affect Your Risk of Heart Disease: What You Should Know
Technology and the Future of Rare Blood Care
Researchers continue to explore alternatives to human donors. Lab-grown red blood cells are one area of focus. If successful, this technology could reduce dependence on rare donors. For now, it remains experimental and limited.
Until then, care depends on planning, cooperation, and trust between people. Technology may help someday, but human coordination still matters most.
Golden blood is not just a scientific curiosity. It reveals how interconnected healthcare systems really are. It shows how a small number of people can make a global difference and exposes how fragile advanced medicine can be.
Final Thoughts
Golden blood sits at the intersection of rarity and responsibility. It can save lives that no other blood can. At the same time, it places those who carry it in uniquely vulnerable positions.
Learning about Rh-null offers more than facts. It offers perspective. Modern medicine depends on preparation, trust, and people willing to help one another. Sometimes, the most valuable resources are also the most fragile.
A.I. Disclaimer: This article was created with AI assistance and edited by a human for accuracy and clarity.
Read More: Studies Indicate That Individuals With This Blood Type Have a Higher Likelihood of Living to 100
Trending Products

Red Light Therapy for Body, 660nm 8...

M PAIN MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGIES Red ...

Red Light Therapy for Body, Infrare...

Red Light Therapy Infrared Light Th...

Handheld Red Light Therapy with Sta...

Red Light Therapy Lamp 10-in-1 with...

Red Light Therapy for Face and Body...

Red Light Therapy Belt for Body, In...

Red Light Therapy for Shoulder Pain...

